I’ve struggled with argumentative essays in the past, just like 79% of high school students according to the National Center for Education Statistics. Selecting a topic, researching different viewpoints, and crafting a persuasive argument often felt overwhelming. But I’ve learned that with the right approach, argumentative essays can be an exciting opportunity to explore important issues and sharpen critical thinking skills.
In this guide, I’ll share 40 thought-provoking argumentative essay topics across various fields, along with strategies for developing strong arguments and leveraging AI tools to enhance your writing. Whether you’re a student looking to ace your next assignment or simply interested in honing your debate skills, you’ll find plenty of inspiration to get those mental gears turning.

Source: letscultivategreatness.com
Choosing Effective Argumentative Essay Topics
Selecting the right topic is crucial for crafting a compelling argumentative essay. I’ve found that the best topics for argumentative essays strike a balance between personal interest and broader relevance. When you’re passionate about a subject, it shows in your writing and makes the research process far more engaging.
Start by considering current events, ongoing debates, or emerging trends that spark your curiosity. I like to browse recent news articles and academic journals to identify hot topics in my field of study. It’s important to evaluate the longevity of potential topics too – will they still be relevant by the time you complete your essay?
Complexity and scope are also key factors to consider. You want a topic with enough depth to explore multiple perspectives, but not so broad that it becomes unmanageable within your word limit. I always conduct some preliminary research to gauge the availability of credible sources and create a basic outline to assess if the topic can be adequately covered.
The most effective argumentative essay topics have clear opposing viewpoints that allow for substantive debate and analysis. This creates opportunities to showcase your critical thinking skills by presenting and refuting counterarguments. When evaluating potential topics, I identify key stakeholders and their positions on the issue, then research common rebuttals to main arguments on both sides of the debate.
For example, if I were writing about whether social media platforms should be held legally responsible for the spread of misinformation, I’d look into arguments from tech companies about Section 230 protections, as well as calls for increased accountability from policymakers and public health experts. This approach ensures I have a well-rounded understanding of the debate before diving into my own argument.
Here’s a quick checklist I use when evaluating potential argumentative essay topics:
□ The topic is relevant to current events or ongoing debates
□ I have a personal interest in the subject matter
□ There are clear opposing viewpoints on the issue
□ Sufficient credible sources are available for research
□ The scope is manageable within the assigned word limit
□ The topic allows for in-depth analysis and critical thinking
□ There’s potential for presenting and refuting counterarguments
□ The subject is appropriate for the intended audience
By carefully considering these factors, you’ll set yourself up for success in crafting a compelling and well-researched argumentative essay. Now, let’s dive into some specific topic ideas across various fields to get your creative juices flowing.
Social Issues
1. Social Media Responsibility
Should social media platforms be held legally responsible for the spread of misinformation on their sites? This question has become increasingly relevant in our digital age, where information (and misinformation) can spread like wildfire.
Currently, major social media companies have varying policies regarding content moderation. Some take a more hands-off approach, citing free speech concerns, while others have implemented fact-checking systems and content removal policies. However, the effectiveness of these measures is hotly debated.
Legal precedents related to platform liability for user-generated content are complex. Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act in the US has historically shielded platforms from liability, but there’s growing pressure to reform this law. Critics argue that social media companies have become too powerful and need to be held accountable for the content they amplify.
On the flip side, increased regulation could have unintended consequences. There are valid concerns about potential impacts on innovation and free expression. Smaller platforms might struggle to comply with strict content moderation requirements, potentially stifling competition in the tech sector.
What do you think? Should we prioritize combating misinformation, even if it means potentially limiting some forms of online expression? Or is the current system of platform immunity the best way to preserve a free and open internet?

Source: theconversation.com
2. Universal Basic Income
Is implementing a universal basic income (UBI) a viable solution to address poverty and economic inequality? This idea has gained traction in recent years, with proponents arguing it could provide a safety net for all citizens and help address growing wealth disparities.
Several countries have conducted UBI pilot programs, with mixed results. Some studies have shown improvements in mental health and job satisfaction among participants, while others have raised concerns about potential work disincentives.
Funding a UBI program on a large scale presents significant challenges. Proposed mechanisms include increased taxation, reallocation of existing welfare spending, or even the creation of sovereign wealth funds. Each approach has its own set of economic and political hurdles to overcome.
Critics of UBI often point to concerns about economic sustainability and potential negative impacts on work incentives. They argue that targeted welfare programs might be more effective at addressing specific needs.
What’s your take on UBI? Could it be the solution to growing economic inequality, or would it create more problems than it solves?
3. Mandatory Vaccination
The debate over mandatory vaccination has intensified in recent years, particularly in light of global health crises. Should governments require all citizens to receive vaccinations for preventable diseases? This controversial topic for argumentative essays touches on the delicate balance between public health concerns and individual freedoms.
Historically, many countries have implemented mandatory vaccination programs for certain diseases, particularly for school-age children. These programs have been credited with dramatically reducing the incidence of diseases like polio and measles.
The scientific consensus strongly supports the efficacy and safety of vaccines. Numerous large-scale studies have demonstrated their effectiveness in preventing serious illnesses and reducing the spread of infectious diseases. However, a small but vocal minority continues to question vaccine safety, often citing debunked studies or anecdotal evidence.
Ethical considerations surrounding bodily autonomy and collective responsibility are at the heart of this debate. Proponents of mandatory vaccination argue that it’s necessary to achieve herd immunity and protect vulnerable populations who cannot be vaccinated. Opponents contend that forcing medical procedures violates personal freedom and sets a dangerous precedent for government overreach.
Where do you stand on this issue? Is mandatory vaccination a necessary public health measure, or an unacceptable infringement on personal liberty?
Technology and Ethics
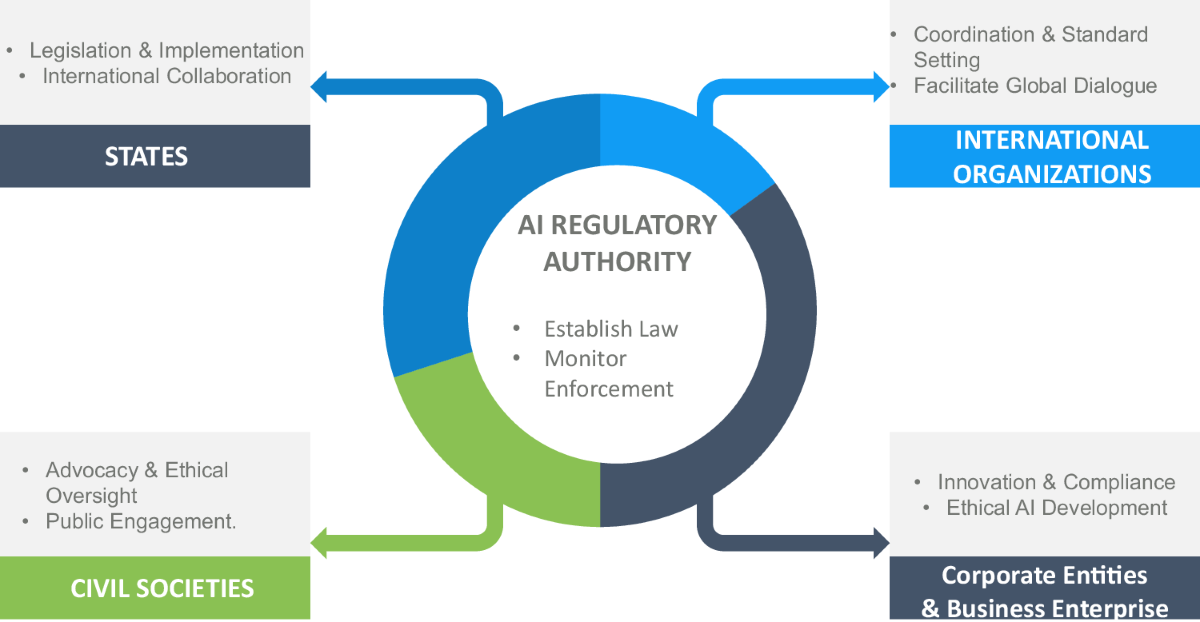
4. AI Regulation
As artificial intelligence continues to advance at a breakneck pace, the question of regulation becomes increasingly urgent. Is it necessary to implement stricter regulations on AI development to mitigate potential risks to humanity?
Current AI governance frameworks are often criticized as inadequate for addressing the complex challenges posed by rapidly evolving technologies. Many experts argue that we need more comprehensive approaches that can keep pace with AI advancements.
The potential risks associated with advanced AI systems are wide-ranging. Job displacement due to automation is already a reality in many industries, and there are growing concerns about algorithmic bias perpetuating or exacerbating existing social inequalities. Some researchers even warn of existential risks posed by the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) that could potentially surpass human capabilities.
Proposed regulatory approaches vary widely. Some advocate for a precautionary principle, arguing that we should slow down AI development until we better understand the risks. Others push for specific regulations around AI transparency, accountability, and ethical guidelines.
The challenge lies in striking a balance between fostering innovation and mitigating potential harms. Overly restrictive regulations could stifle important research and development, potentially ceding technological leadership to less cautious nations. On the other hand, a lack of adequate oversight could lead to unintended consequences with far-reaching impacts on society.
What level of AI regulation do you think is appropriate? How can we balance innovation with responsible development?
Source: springernature.com
5. Gene Editing Ethics
The rapid advancement of gene editing technologies like CRISPR has opened up unprecedented possibilities for modifying human DNA. But should we permit the use of these powerful tools on human embryos for non-medical purposes?
Current regulations on human embryo research vary widely between countries. Some nations have implemented outright bans, while others allow research under strict guidelines. The international scientific community has called for a moratorium on clinical applications of human germline editing until ethical and safety concerns can be adequately addressed.
The potential benefits of gene editing for trait enhancement are tantalizing. Proponents argue that it could lead to healthier, longer-lived humans with enhanced cognitive abilities. However, the risks and unknowns are significant. We’re still learning about the complex interplay of genes and their long-term effects on human development.
One of the most pressing concerns is the potential for creating “designer babies” and exacerbating social inequalities. If gene editing for enhancement becomes available, it’s likely that only the wealthy would have access initially, potentially creating a genetically enhanced upper class.
There are also worries about unintended consequences. Modifying genes for one trait could have unforeseen effects on other aspects of human biology. And once we start making heritable changes to the human genome, those modifications would be passed down to future generations.
Where do you draw the line on gene editing? Is it ethical to use this technology for enhancement, or should it be restricted to medical applications only?
6. Autonomous Vehicles
The development of self-driving cars has made remarkable progress in recent years, but a crucial question remains: Should fully autonomous vehicles be allowed on public roads before achieving 100% safety?
Current safety statistics for autonomous vehicles are promising, with many studies suggesting they’re already safer than human drivers in certain conditions. However, high-profile accidents involving self-driving cars have raised public concerns and highlighted the challenges of integrating this technology into existing transportation systems.
The potential benefits of widespread autonomous vehicle adoption are significant. Proponents argue that it could dramatically reduce traffic accidents, improve mobility for the elderly and disabled, and increase overall transportation efficiency. However, these benefits must be weighed against the risks of deploying a technology that’s not yet perfect.
Liability and insurance implications of autonomous vehicle accidents are complex and largely unresolved. Who’s responsible when a self-driving car causes an accident – the manufacturer, the software developer, or the vehicle owner? These questions have significant legal and ethical implications.
Another factor to consider is the potential societal impact, particularly job displacement in transportation industries. Millions of people worldwide work as drivers, and the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could lead to significant unemployment in these sectors.
Given these considerations, what level of safety should we require before allowing fully autonomous vehicles on public roads? Is “safer than human drivers” good enough, or should we hold this technology to a higher standard?
These interesting argumentative essay topics highlight the complex ethical dilemmas we face as technology continues to advance. They offer rich ground for debate and critical analysis, challenging us to consider the far-reaching implications of our technological choices.
Education
7. Standardized Testing Efficacy
Do standardized tests accurately measure student performance and predict future success? This question has been hotly debated in educational circles for years, with passionate arguments on both sides.
Proponents of standardized testing argue that it provides an objective measure of student achievement, allowing for comparisons across schools and districts. They point to correlations between test scores and future academic and career success as evidence of their predictive value.
However, critics raise valid concerns about potential biases in test design and administration. Standardized tests have been shown to disadvantage students from lower socioeconomic backgrounds and non-native English speakers. There’s also the question of whether these tests truly measure important skills like critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving ability.
Alternative assessment methods have gained traction in recent years. Project-based assessments, portfolio evaluations, and performance tasks are just a few examples of approaches that aim to provide a more holistic view of student abilities.
Let’s take a closer look at how different assessment methods stack up:
|
Assessment Method |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
Standardized Tests |
Objective, Comparable across schools |
May not reflect real-world skills, Potential cultural bias |
|
Project-Based Assessments |
Measures practical skills, Encourages creativity |
Time-consuming to grade, Subjectivity in evaluation |
|
Portfolio Assessments |
Comprehensive view of student work, Shows growth over time |
Storage and organization challenges, Time-intensive review process |
|
Oral Examinations |
Assesses communication skills, Allows for follow-up questions |
Potential for examiner bias, Time-consuming for large classes |
|
Peer Assessments |
Develops critical thinking, Reduces grading workload for teachers |
Potential for unfair evaluations, Requires training for students |
What role do you think standardized tests should play in our education system? Are they a necessary evil, or should we be moving towards alternative forms of assessment?
8. Free Higher Education
The idea of providing free college education to all citizens has gained traction in many countries. But is it a realistic and beneficial policy?
Several countries, particularly in Europe, have implemented systems of free or heavily subsidized higher education. Proponents argue that this approach increases access to education, reduces student debt burdens, and ultimately benefits society by creating a more educated workforce.
However, the economic implications of such a policy are significant. Funding mechanisms typically rely on increased taxation, which can be politically challenging to implement. There are also concerns about the potential impact on educational quality and resource allocation in a free system.
Critics argue that free higher education could lead to overcrowding in universities and potentially devalue college degrees. They also point out that such a system might unfairly benefit middle and upper-class families who are more likely to send their children to college anyway.
What’s your take on this issue? Is free higher education a worthwhile investment in our future, or an unsustainable policy that could have unintended negative consequences?
9. Homeschooling vs. Traditional Education
The debate between homeschooling and traditional education has intensified in recent years, particularly in light of global events that have disrupted normal schooling. Is homeschooling a viable alternative to traditional schooling for K-12 education?
Academic performance data for homeschooled vs. traditionally educated students presents a mixed picture. Some studies show that homeschooled students tend to score higher on standardized tests, while others find no significant difference when controlling Understood. I’ll continue covering the remaining content without starting over:
for factors like parental education and income.
One of the most common concerns about homeschooling is socialization. Critics argue that homeschooled children miss out on important social interactions and extracurricular opportunities. However, many homeschooling families counter that they provide ample socialization through community groups, sports teams, and other activities.
Regulatory frameworks for homeschooling vary widely across different jurisdictions. Some areas have strict requirements for curriculum and assessment, while others take a more hands-off approach. This lack of standardization can make it challenging to ensure educational quality across all homeschooling situations.
Consider the case of John, a homeschooled student who excelled academically but struggled with social interactions when he entered college. Contrast this with Sarah, who attended public school and developed strong social skills but felt unchallenged in her classes. These examples highlight the nuanced trade-offs between homeschooling and traditional education.
What do you think? Can homeschooling provide a comparable or even superior education to traditional schooling, or are the social and structural benefits of traditional schools irreplaceable?
Writing Strong Thesis Statements
These argumentative essay topics for students offer rich ground for debate and analysis. They challenge us to think critically about the purpose and methods of education in our rapidly changing world.
Environment and Sustainability
10. Climate Change Accountability
The question of who bears greater responsibility for mitigating climate change has become a contentious issue in international negotiations. Should developed nations shoulder a heavier burden in addressing this global crisis?
Historical emissions data paints a clear picture: industrialized countries have contributed disproportionately to greenhouse gas accumulation in the atmosphere. The United States, for instance, has emitted more CO2 cumulatively than any other nation. This historical responsibility forms a key argument for why developed countries should lead the charge in emissions reduction and climate adaptation efforts.
Economic disparities between nations further complicate the issue. Developing countries argue that aggressive climate action could hinder their economic growth and ability to lift citizens out of poverty. They call for technology transfer and financial support from wealthier nations to enable sustainable development pathways.
Proposed mechanisms for equitable climate action include climate finance initiatives and differentiated emissions reduction targets. The Green Climate Fund, established under the Paris Agreement, aims to channel resources from developed to developing countries for climate projects. However, debates persist over funding levels and implementation.
Critics of this approach argue that rapidly growing economies like China and India must also take significant action, given their current and projected emissions. They contend that a truly effective climate strategy requires full participation from all major emitters, regardless of historical contributions.
Where do you stand on this complex issue? How can we balance historical responsibility with current realities to create an effective and fair global climate strategy?
Source: noaa.gov
11. Nuclear Energy Viability
As the world grapples with the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, the role of nuclear power remains hotly debated. Is nuclear energy a sustainable and safe solution for our climate crisis?
Comparing carbon emissions across energy sources reveals nuclear power’s potential. Nuclear plants produce minimal greenhouse gases during operation, rivaling renewables like wind and solar in terms of lifecycle emissions. They also provide reliable baseload power, addressing intermittency issues associated with some renewable sources.
However, safety concerns loom large in public perception. High-profile accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima have eroded trust in nuclear technology. Modern reactor designs incorporate numerous safety features, significantly reducing the risk of catastrophic failures. Yet, the consequences of a worst-case scenario remain severe.
Long-term waste management presents another challenge. While technological advancements have improved storage and potential recycling options for spent nuclear fuel, the issue of safely containing radioactive waste for thousands of years remains contentious.
Proponents argue that nuclear power is essential for rapid decarbonization, pointing to countries like France that have successfully reduced emissions through nuclear energy. Skeptics counter that the high costs and long construction times for nuclear plants make them less attractive than rapidly advancing renewable technologies.
What role, if any, should nuclear energy play in our transition to a low-carbon future? Can the benefits outweigh the risks and public concerns?
12. Single-Use Plastic Bans
The proliferation of single-use plastics has become a visible symbol of our throwaway culture and its environmental consequences. But are comprehensive bans the answer?
Examining the environmental impact reveals a sobering picture. Plastic pollution chokes our oceans, harms wildlife, and even enters the human food chain through microplastics. The production and disposal of single-use plastics also contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Several jurisdictions have implemented bans on items like plastic bags and straws. Early data suggests these measures can reduce plastic waste, but they’re not without economic consequences. Some businesses report increased costs associated with alternative materials.
The effectiveness of existing bans varies. While plastic bag usage has declined in many areas with restrictions, critics argue that some alternatives (like thicker reusable plastic bags) may have a larger carbon footprint if not used multiple times.
Potential alternatives to single-use plastics include biodegradable materials, reusable container systems, and packaging-free retail models. However, scaling these solutions presents challenges in terms of cost, convenience, and consumer behavior change.
Is a blanket ban on single-use plastics the most effective approach to tackle this environmental crisis? Or should we focus on targeted restrictions, improved recycling infrastructure, and incentives for sustainable alternatives?
These great topics for argumentative essays highlight the complex trade-offs involved in environmental policy decisions. They challenge us to consider both the immediate and long-term consequences of our choices in addressing pressing sustainability issues.
Politics and Governance
13. Voting Age Reduction
The proposal to lower the legal voting age to 16 has gained traction in some countries. Proponents argue that it would increase youth civic engagement and ensure their voices are heard on issues that will shape their futures.
Analyzing political engagement among 16-17 year olds reveals mixed results. Some studies show that this age group can be as informed and motivated as older voters when given the opportunity to participate. However, critics worry about maturity levels and susceptibility to influence.
Several countries, including Austria and Scotland (for some elections), have already lowered their voting age. These case studies provide valuable data on youth turnout and the impact on political discourse.
A key argument in favor of lowering the voting age is that 16-year-olds are already taking on adult responsibilities in many areas. They can work, pay taxes, and in some places, join the military. Shouldn’t they have a say in the policies that affect them?
Opponents counter that the brain’s prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making and long-term planning, isn’t fully developed until the mid-20s. They argue that this could lead to impulsive voting based on short-term concerns rather than careful consideration of complex issues.
What’s your stance on this issue? Would lowering the voting age strengthen our democracy, or potentially undermine the integrity of our electoral process?
14. Term Limits for Elected Officials
The question of whether to impose term limits on all elected government positions sparks heated debate in many democracies. Advocates argue that it prevents career politicians from becoming entrenched and brings fresh perspectives to governance.
Analyzing the impact of term limits on legislative effectiveness yields mixed results. Some studies suggest that frequent turnover can lead to a loss of institutional knowledge and weaken the legislature’s ability to serve as a check on executive power. Others find that it can increase diversity in representation and reduce the influence of special interests.
Term limits could potentially affect corruption levels and the entrenchment of political power. Proponents argue that limiting time in office reduces opportunities for corruption to take root. Critics counter that it might incentivize officials to focus on short-term gains or post-office opportunities rather than long-term policy solutions.
Alternative methods for ensuring political accountability and turnover exist. These include campaign finance reform, open primaries, and improved civic education to encourage more informed voting.
Ultimately, the debate centers on balancing the value of experience against the need for new ideas and perspectives in government. What’s your take? Are term limits a necessary safeguard against political stagnation, or do they deprive voters of the right to keep effective leaders in office?
15. Electoral College Reform
The United States’ Electoral College system has come under increased scrutiny in recent years, particularly after elections where the popular vote winner didn’t secure the presidency. Should this system be abolished or reformed?
Historical analysis reveals several instances of Electoral College/popular vote mismatches, most recently in 2000 and 2016. These outcomes have intensified calls for change, with critics arguing that the current system gives disproportionate weight to less populous states.
Proposed alternatives include a direct national popular vote or the National Popular Vote Interstate Compact. This agreement between states would award their electoral votes to the national popular vote winner, effectively bypassing the need for a constitutional amendment.
Supporters of the Electoral College argue that it protects the interests of smaller states and prevents candidates from focusing solely on high-population urban centers. They contend that it encourages coalition-building and maintains the federal character of the United States.
Critics counter that the winner-take-all allocation of electoral votes in most states leads to the neglect of non-competitive states in presidential campaigns. They argue that a national popular vote would make every vote count equally, regardless of where it’s cast.
Potential impacts on campaign strategies and voter representation are significant. A shift to a popular vote system could dramatically alter how and where candidates focus their efforts.
What’s your position on this fundamental aspect of the U.S. electoral system? Does the Electoral College still serve a valuable purpose, or is it time for a change?
These argumentative research topics delve into core issues of democratic governance. They challenge us to consider how our political systems can best represent the will of the people and adapt to changing societal needs.
Emerging Technologies
16. Brain-Computer Interfaces
The rapid advancement of brain-computer interface (BCI) technology raises profound questions about cognitive privacy and the boundaries between human thought and external devices. Should we implement regulations to protect our mental autonomy?
Current applications of BCIs in medicine and assistive technology show immense promise. These devices have enabled paralyzed individuals to control prosthetic limbs and communicate through thought alone. The potential to restore lost functions and enhance human capabilities is truly revolutionary.
However, as BCIs become more sophisticated, concerns about privacy and data security intensify. The idea that our thoughts could be monitored, recorded, or even influenced by external devices is both fascinating and terrifying. What safeguards should be in place to protect our most intimate mental processes?
Proposed regulatory frameworks for neurotechnology vary widely. Some advocate for a “right to cognitive liberty” enshrined in law, while others push for strict controls on BCI development and deployment. Finding the right balance between fostering innovation and protecting individual rights presents a significant challenge.
The ethical implications extend beyond privacy concerns. As BCIs blur the line between human cognition and artificial intelligence, we may need to reconsider our definitions of personhood and consciousness. How will society adapt to a world where thoughts can be directly translated into digital actions?
What level of regulation do you think is appropriate for BCI technology? How can we harness its potential benefits while safeguarding our cognitive autonomy?
17. Humanoid Robots
The development of increasingly sophisticated humanoid robots forces us to grapple with complex questions about the future of human-machine interactions. Are these lifelike machines a boon or a bane for society?
Current capabilities of humanoid robots are impressive but limited. They can perform specific tasks with great precision, but general-purpose humanoid robots that can seamlessly integrate into human environments remain largely in the realm of science fiction.
Potential applications span various industries. In healthcare, humanoid robots could assist with patient care and rehabilitation. Educational settings might employ them as tutors or language practice partners. Service industries could use humanoid robots for customer interactions in retail or hospitality settings.
Job displacement concerns loom large in discussions about humanoid robots. While they may create new jobs in robot design and maintenance, the potential for widespread automation in service sectors could lead to significant workforce disruptions.
Ethical considerations surrounding human-robot interactions are complex. As robots become more lifelike, questions arise about appropriate boundaries in our relationships with them. Could people develop unhealthy emotional attachments to humanoid robots? How might this impact human-to-human relationships?
Another factor to consider is the potential for humanoid robots to perpetuate or exacerbate societal biases. If not carefully designed and programmed, these robots could reflect and amplify existing prejudices in their interactions with humans.
What role do you envision for humanoid robots in our future society? How can we maximize their benefits while mitigating potential negative impacts on employment and social dynamics?
18. Space Colonization
As private companies join government agencies in pushing the boundaries of space exploration, the question of prioritizing space colonization efforts becomes increasingly relevant. Should we invest heavily in establishing human settlements beyond Earth?
Examining the technological hurdles reveals the enormity of the challenge. Long-term space habitation requires solving complex problems in life support systems, radiation protection, and psychological well-being in isolated environments. The resource requirements for such endeavors are staggering.
Potential scientific and economic benefits of space colonization are tantalizing. Advances in materials science, energy production, and resource utilization could have far-reaching impacts on Earth-based technologies. The possibility of accessing extraterrestrial resources could revolutionize industries and potentially alleviate resource scarcity on our home planet.
However, ethical concerns about prioritizing space exploration over pressing Earth-based issues persist. Critics argue that the immense resources required for space colonization efforts could be better spent addressing climate change, poverty, or healthcare challenges on Earth.
The Mars One project serves as a cautionary tale. Despite initial enthusiasm and thousands of applicants, the project faced insurmountable challenges in funding, technology, and long-term sustainability, ultimately leading to its bankruptcy in 2019. This case illustrates the complex realities of space colonization efforts.
Proponents of space colonization often argue that it’s necessary for the long-term survival of our species, providing a “backup plan” in case of global catastrophe on Earth. Skeptics counter that we should focus on preserving our current planet rather than seeking an escape route.
Where do you stand on this cosmic question? Is space colonization a visionary goal we should actively pursue, or a distraction from more immediate earthly concerns?
These unique argumentative essay topics highlight the profound ways emerging technologies are reshaping our world and our understanding of what it means to be human. They challenge us to think critically about the future we want to create and the ethical frameworks needed to guide technological development.
Global Health and Bioethics
19. Mandatory Genetic Screening
The advent of rapid, low-cost genetic testing has sparked debate about whether genetic screening should be required for all newborns. This policy could potentially revolutionize preventive healthcare, but it also raises significant ethical concerns.
Current newborn screening programs vary widely between countries and even within regions. Most focus on a limited set of treatable conditions, but advances in genetic testing have dramatically expanded the number of detectable disorders.
Proponents argue that mandatory genetic screening could lead to earlier interventions for a wide range of conditions, potentially improving health outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. It could also provide valuable data for medical research, advancing our understanding of genetic diseases.
However, the ethical implications are profound. Concerns about genetic privacy and potential discrimination loom large. How can we ensure that genetic information isn’t misused by employers, insurers, or other parties? There’s also the psychological impact to consider – how might knowledge of genetic predispositions affect an individual’s life choices and mental well-being?
The economic aspects are equally complex. While early detection and intervention could potentially reduce long-term healthcare costs, implementing universal genetic screening would require significant upfront investment.
What’s your stance on this issue? Do the potential health benefits of mandatory genetic screening outweigh the privacy Understood. I’ll continue from where I left off:
concerns and ethical risks?
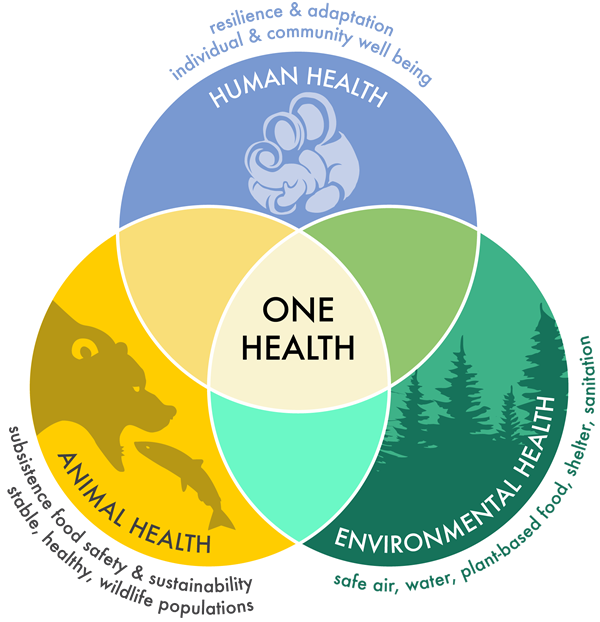
20. International Healthcare Aid
The stark disparities in global health outcomes raise challenging questions about the obligations of wealthy nations. Should they be compelled to provide substantial healthcare aid to developing countries?
Analyzing current levels of international healthcare aid reveals a mixed picture. While significant resources are directed towards global health initiatives, many argue that it’s insufficient given the scale of need. The impact of existing programs varies widely, with some achieving remarkable successes in areas like vaccine distribution and others struggling with implementation challenges.
Moral arguments for increased aid often center on the idea of health as a fundamental human right and the ethical imperative to reduce suffering where possible. Proponents also point to the interconnected nature of global health – diseases don’t respect borders, so investing in health systems worldwide benefits everyone.
Economic considerations complicate the debate. Critics worry about aid dependency and argue that large-scale health assistance might undermine the development of sustainable, locally-driven healthcare systems. There’s also the question of how to balance international aid with domestic healthcare needs in donor countries.
Potential mechanisms for coordinating and delivering global health assistance range from expanding existing multilateral organizations to creating new targeted initiatives. Each approach has its own set of advantages and challenges in terms of efficiency, accountability, and political feasibility.
What level of obligation do you think wealthy nations have to provide healthcare aid? How can we structure international health assistance to maximize its effectiveness and promote long-term sustainability?
Source: pubh110.digital.uic.edu
21. Human Enhancement Ethics
Advances in biotechnology are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of human enhancement. But is the use of these technologies for non-medical purposes ethically justifiable?
Current and emerging human enhancement technologies span a wide range. Cognitive enhancers, physical augmentations, and even genetic modifications are moving from the realm of science fiction into reality. Each category brings its own set of ethical considerations.
Proponents argue that human enhancement technologies could lead to significant improvements in quality of life, productivity, and even human potential. They contend that if we have the ability to enhance our capabilities, we have an obligation to do so.
Critics raise concerns about social equality and human diversity. If enhancement technologies are only available to the wealthy, could we see the emergence of a “genetic divide” that exacerbates existing inequalities? There’s also the question of how enhancement might affect our understanding of human identity and what it means to be “normal.”
Evaluating the permissibility of enhancement technologies requires grappling with fundamental philosophical questions. What constitutes a legitimate medical use versus an enhancement? How do we weigh individual autonomy against potential societal impacts?
Some propose a “reversal test” thought experiment: if we could safely reduce human intelligence across the board, would we consider that ethical? If not, why would enhancing intelligence be unethical? This kind of reasoning challenges us to examine our intuitions about human enhancement.
Where do you draw the line on human enhancement? Are there some forms of enhancement that are more ethically acceptable than others?
Economic Systems and Policies
22. Cryptocurrency Integration
The rise of digital currencies has sparked intense debate about their role in national financial systems. Should governments embrace cryptocurrencies or maintain a cautious distance?
Examining the impact of cryptocurrency adoption reveals a complex picture. Proponents argue that integrating digital currencies could increase financial inclusion, reduce transaction costs, and spur innovation in the financial sector. Critics worry about the potential for increased money laundering, tax evasion, and financial instability.
Several countries have taken divergent approaches to cryptocurrency regulation. Some, like El Salvador, have made bold moves to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender. Others, such as China, have imposed strict bans on cryptocurrency trading and mining. These case studies offer valuable insights into the potential consequences of different regulatory strategies.
Central banks worldwide are exploring the possibility of issuing their own digital currencies (CBDCs). This approach could allow governments to harness some benefits of digital currency technology while maintaining greater control over monetary policy.
The environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining, particularly for proof-of-work systems like Bitcoin, adds another layer to the debate. Can the energy consumption associated with these technologies be justified?
What’s your take on government involvement with cryptocurrencies? Is integration inevitable, or should traditional financial systems remain separate from the world of digital assets?
23. Four-Day Workweek
The concept of a four-day workweek has gained traction in recent years, with proponents arguing it could improve work-life balance without sacrificing productivity. But is this model economically viable on a large scale?
Results from four-day workweek trials in various companies and countries have been promising. Many report maintained or even increased productivity, along with improvements in employee well-being and job satisfaction. Iceland’s large-scale trial, involving around 1% of the workforce, was deemed an “overwhelming success” by researchers.
However, implementing reduced work hours across different industries presents significant challenges. Sectors like healthcare, emergency services, and hospitality may struggle to adapt to a four-day model without increasing costs or reducing service availability.
The potential impacts on business costs are multifaceted. While some companies might see reduced overhead expenses, others could face challenges in scheduling and coverage, potentially leading to increased overtime pay or the need to hire additional staff.
Broader economic effects must also be considered. Could a widespread shift to a four-day week stimulate consumer spending and boost certain sectors of the economy? Or might it lead to reduced economic output overall?
What’s your perspective on the four-day workweek? Is it a progressive policy that could benefit both workers and businesses, or an idealistic concept that’s impractical for many industries?
24. Global Minimum Wage
The idea of an internationally enforced global minimum wage has been proposed as a potential solution to address income inequality and improve working conditions worldwide. But is such a policy feasible or desirable?
Analyzing current minimum wage policies across different countries reveals vast disparities. While some nations have relatively high minimum wages, others have very low or no minimum wage laws at all. These differences reflect varying economic conditions, living costs, and political philosophies.
Implementing a global minimum wage would face numerous hurdles. Determining an appropriate wage level that accounts for differing economic conditions across countries would be extremely challenging. Enforcement mechanisms would also need to be developed, raising questions about national sovereignty and the role of international organizations.
Potential impacts on international trade and labor markets could be significant. A global minimum wage might help reduce the “race to the bottom” in terms of labor costs, potentially improving working conditions in developing countries. However, it could also lead to job losses in some regions if set too high, or accelerate the trend towards automation.
Critics argue that a one-size-fits-all approach to wages could harm developing economies by making them less competitive in the global market. They contend that wage levels should be determined by local economic conditions and through collective bargaining processes.
Proponents counter that a carefully implemented global minimum wage could help ensure that workers worldwide receive a living wage, reducing exploitation and improving global economic equity.
What’s your stance on this ambitious proposal? Could a global minimum wage help create a more equitable world economy, or would it cause more problems than it solves?
|
Policy Approach |
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|---|
|
Global Minimum Wage |
Reduces income inequality, Improves working conditions globally |
Difficult to enforce, May harm developing economies |
|
National Minimum Wages |
Tailored to local economic conditions, Easier to implement |
Uneven global standards, Potential for exploitation in low-wage countries |
|
Universal Basic Income |
Provides basic security for all, Simplifies welfare systems |
High implementation costs, Potential work disincentives |
|
Progressive Taxation |
Targets wealth concentration, Flexible implementation |
Complex to administer, Potential for tax avoidance |
|
Collective Bargaining |
Empowers workers, Allows for industry-specific negotiations |
Requires strong labor organizations, Can lead to labor disputes |
Media and Culture
25. Cancel Culture Ethics
The phenomenon of “cancel culture” has become a lightning rod for debates about accountability, free speech, and the power of public opinion in the digital age. Does this trend promote necessary accountability or threaten open dialogue?
Examining high-profile cases of “cancellation” reveals a spectrum of outcomes. Some instances have led to meaningful conversations about systemic issues and accountability for powerful figures. Others have been criticized as disproportionate responses to minor transgressions or misunderstandings.
Social media plays a crucial role in amplifying public outrage and organizing boycotts. The speed and reach of online platforms can turn local incidents into global controversies within hours. This rapid escalation raises questions about due process and the potential for mob mentality.
Proponents argue that cancel culture serves as a necessary tool for marginalized groups to hold powerful individuals and institutions accountable. They contend that it’s simply a modern form of boycott or protest, enabled by social media.
Critics worry about the chilling effect on free speech and artistic expression. They argue that the threat of being “canceled” can lead to self-censorship and stifle important debates. There are also concerns about the lack of nuance in many cancellation campaigns and the potential for false accusations to cause lasting damage.
The impact on public discourse is a key point of contention. Has cancel culture made people more mindful of their words and actions, or has it created an atmosphere of fear and conformity?
What’s your take on this contentious issue? Is cancel culture a necessary corrective in an unequal society, or a threat to free expression and open dialogue?

Source: alamy.com
26. Social Media Algorithm Regulation
The power of social media algorithms to shape our information diets and influence public opinion has come under increasing scrutiny. Should governments step in to regulate these algorithms in the interest of reducing polarization and misinformation?
Understanding how social media algorithms currently function is crucial to this debate. These complex systems are designed to maximize user engagement, often by showing content that aligns with a user’s existing views or interests. This can lead to the creation of “filter bubbles” where users are primarily exposed to information that confirms their existing beliefs.
The impact of these echo chambers on political polarization and social cohesion is a growing concern. Studies suggest that algorithmic curation can amplify extreme views and contribute to the spread of misinformation.
Proposed regulatory approaches vary widely. Some advocate for increased transparency, requiring companies to disclose how their algorithms work. Others push for more direct intervention, such as mandating the inclusion of diverse viewpoints in users’ feeds.
Critics of regulation argue that government intervention could infringe on free speech rights and stifle innovation in the tech sector. They contend that users should have the freedom to choose their information sources without government interference.
Proponents counter that the outsized influence of a few large tech companies on public discourse necessitates some form of oversight. They argue that leaving these powerful algorithms unchecked poses a threat to democratic processes and social stability.
What level of algorithmic regulation, if any, do you think is appropriate? How can we balance the need for a well-informed public with concerns about government overreach and free speech?
27. Cultural Appropriation
The concept of cultural appropriation has sparked heated debates about the boundaries between cultural exchange, appreciation, and exploitation. Where do we draw the line between respectful borrowing and harmful appropriation?
High-profile cases of alleged cultural appropriation in fashion, music, and art have brought this issue to the forefront of public discourse. From hairstyles to musical genres, the question of who has the “right” to use certain cultural elements is complex and often contentious.
Historical context and power dynamics play a crucial role in these discussions. Critics of cultural appropriation argue that when dominant cultures adopt elements from marginalized groups without understanding or respecting their significance, it perpetuates harmful stereotypes and erases the original cultural context.
Proponents of cultural exchange contend that borrowing and mixing elements from different cultures is a natural and positive aspect of human creativity. They argue that attempts to police cultural boundaries can lead to a stifling of artistic expression and intercultural understanding.
Proposed guidelines for respectful cultural borrowing often emphasize the importance of attribution, education, and collaboration with members of the originating culture. But implementing these principles in practice can be challenging.
The debate extends beyond individual actions to questions of systemic power and representation. How do we ensure that marginalized cultures benefit from the mainstream adoption of their cultural elements?
What’s your perspective on this nuanced issue? Is cultural appropriation a form of theft and disrespect, or a natural part of cultural evolution and exchange?
Effective Use of Examples in Essays
These topics delve into the complex interplay between media, technology, and culture in our increasingly interconnected world. They challenge us to consider how we can foster a diverse and respectful global culture while navigating the pitfalls of rapid information sharing and cultural exchange.
Future of Work and Education
28. Mandatory Coding Education
As technology continues to reshape the job market, the question of whether coding should be a mandatory subject in K-12 education has gained prominence. Would universal coding literacy benefit society, or is it an unnecessary addition to an already packed curriculum?
Current initiatives to integrate coding into school curricula vary widely. Some countries, like Estonia, have made programming a core part of their national education strategy. Others have introduced coding as an elective or extracurricular activity.
Proponents argue that coding skills will be essential for many future jobs, even outside the tech sector. They contend that learning to code develops problem-solving abilities and computational thinking skills that are valuable across disciplines.
Critics worry about curriculum overload and question whether coding should take precedence over other subjects. They argue that a one-size-fits-all approach to coding education might not serve all students’ needs and interests.
The effectiveness of early coding education on problem-solving skills is still being studied. While some research suggests positive outcomes, more long-term studies are needed to fully understand the impact.
Another factor to consider is the rapid pace of technological change. Will the coding languages and concepts taught today still be relevant when today’s elementary students enter the workforce?
What’s your stance on mandatory coding education? Is it a necessary preparation for the future job market, or should it remain an optional subject?

Source: raspberrypi.org
29. Gig Economy Ethics
The rise of the gig economy has transformed the nature of work for millions of people worldwide. But is this model empowering workers with flexibility, or exploiting them through precarious employment?
Analyzing income data and working conditions for gig economy workers reveals a mixed picture. While some thrive on the flexibility and entrepreneurial opportunities, others struggle with income instability and lack of benefits.
Legal challenges surrounding gig worker classification have emerged in many countries. The question of whether these workers should be considered employees or independent contractors has significant implications for labor protections and company business models.
Proponents of the gig economy argue that it provides opportunities for those who might struggle in traditional employment settings. They contend that the flexibility allows workers to balance multiple jobs or pursue other interests.
Critics point to the lack of job security, benefits, and worker protections Understood. I’ll continue from where I left off:
in many gig economy arrangements. They argue that companies are shifting business risks onto workers while reaping the benefits of their labor.
The long-term impact of gig work on career development and social safety nets is a growing concern. How will workers build stable careers and save for retirement in an economy dominated by short-term, project-based work?
What’s your take on the ethics of the gig economy? Can it be reformed to better protect workers, or is it fundamentally exploitative?
30. Vocational vs. Traditional Education
The balance between vocational training and traditional academic programs in higher education is a subject of ongoing debate. Should universities shift their focus towards more job-specific skills, or maintain their emphasis on broader theoretical knowledge?
Examining employment outcomes for vocational vs. traditional degree graduates yields interesting insights. Some studies show that vocational graduates often have higher initial employment rates and starting salaries. However, traditional degree holders may have more career flexibility and advancement opportunities in the long term.
The evolving skill requirements in various industries complicate this picture. Many employers report a skills gap between what graduates learn in school and what’s needed in the workplace. This has led to calls for more practical, hands-on training in higher education.
Proponents of increased vocational focus argue that it would better prepare students for the job market and reduce student debt by shortening the time to employment. They contend that many jobs don’t require the broad theoretical background provided by traditional degrees.
Critics worry that an overemphasis on vocational training could undermine the role of universities in fostering critical thinking, research, and innovation. They argue that a well-rounded education provides skills that are valuable across multiple careers and prepares students for a rapidly changing job market.
The potential impact on research and innovation is another consideration. How might a shift towards more vocational education affect the pipeline of academic researchers and the advancement of theoretical knowledge?
What balance do you think universities should strike between vocational training and traditional academic programs? How can higher education best prepare students for the future of work?
These topics explore the changing landscape of work and education in the 21st century. They challenge us to reconsider traditional models and adapt our educational systems to meet the needs of a rapidly evolving global economy.
Strategies for Writing Compelling Arguments
Crafting a Strong Thesis Statement
The cornerstone of any good argumentative essay is a clear, concise thesis statement. It serves as the roadmap for your entire argument, guiding both you and your readers through your reasoning.
When developing your thesis, ensure it’s specific and debatable. Avoid overly broad claims or statements of fact. Instead, stake out a position that someone could reasonably argue against.
As you delve deeper into your research, don’t be afraid to refine your thesis. New information might lead you to modify or even completely change your initial position. This evolution is a natural part of the writing process and often results in a stronger final argument.
Use clear, straightforward language in your thesis statement. Avoid jargon or overly complex phrasing that might confuse your readers. Your goal is to present your position in a way that’s immediately understandable.
Remember, a good argumentative essay doesn’t just state an opinion – it makes a case. Your thesis should hint at the evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support your position.
This video offers valuable insights on crafting effective thesis statements, complementing the written content with visual examples and expert advice.
[Video Source: https://www.youtube.com/embed/zhN3CNV4FMw]
Addressing Counterarguments
A robust argument doesn’t shy away from opposing viewpoints – it anticipates and addresses them head-on. This approach not only strengthens your position but also demonstrates your thorough understanding of the topic.
Start by researching common objections to your stance. What evidence do opponents typically cite? Understanding these counterarguments allows you to prepare thoughtful responses.
When presenting counterarguments in your essay, do so fairly and accurately. Misrepresenting opposing views undermines your credibility. Instead, acknowledge the strengths of other perspectives before explaining why your position is ultimately more convincing.
Consider dedicating a paragraph or section to addressing the strongest counterarguments. This shows readers that you’ve carefully considered multiple angles of the issue.
By engaging with opposing viewpoints, you create a more nuanced and persuasive argument. It also helps you identify potential weaknesses in your own reasoning, allowing you to shore up your position.
Using Rhetorical Devices Effectively
Rhetorical techniques can elevate your writing from merely informative to truly persuasive. By appealing to different aspects of your audience’s psyche, you can create a more compelling and memorable argument.
Ethos, pathos, and logos form the foundation of persuasive rhetoric. Ethos establishes your credibility as a writer. Cite reputable sources and demonstrate your understanding of the topic to build trust with your readers.
Pathos appeals to emotions. While your argument should be grounded in logic, don’t underestimate the power of emotional resonance. Personal anecdotes or vivid examples can help readers connect with your position on a deeper level.
Logos focuses on logical reasoning and evidence. Present your facts and statistics clearly, explaining how they support your argument. Use deductive or inductive reasoning to guide readers through your thought process.
Rhetorical questions can be a powerful tool for engaging readers and prompting reflection. Use them sparingly to emphasize key points or challenge assumptions.
Incorporating real-world examples or case studies can illustrate your arguments more vividly than abstract concepts alone. These concrete illustrations help readers grasp the practical implications of your position.
Enhancing Arguments with Rhetoric
Leveraging AI Tools for Essay Excellence
Brainstorming and Outlining Assistance
AI-powered writing assistants can jumpstart your essay development process. These tools offer topic suggestions based on your initial ideas, helping you explore different angles you might not have considered.
When using AI for brainstorming, treat its suggestions as a starting point rather than a final product. Combine AI-generated ideas with your own insights to create a unique perspective on your chosen topic.
AI can also help create structured outlines for your argumentative essays. These automated outlines provide a solid foundation, but it’s crucial to refine them to ensure logical flow and comprehensive coverage of your arguments.
Remember that while AI can offer valuable assistance, your critical thinking and analysis are what will ultimately make your essay stand out. Use AI as a tool to enhance your own ideas, not replace them.
Research and Citation Support
Navigating the vast sea of information available online can be daunting. AI-curated databases can help you quickly find credible sources relevant to your topic, saving valuable research time.
Automatic citation generators streamline the often tedious process of formatting references. However, always double-check these auto-generated citations for accuracy. Different style guides have nuanced requirements that AI might not always capture perfectly.
While AI can suggest sources, it’s essential to cross-reference these with authoritative academic databases. This ensures the quality and reliability of your sources, which is crucial for building a strong argument.
Language Enhancement and Plagiarism Prevention
Advanced language models offer suggestions to improve your writing’s clarity and style. They can help identify awkward phrasing, suggest more precise vocabulary, and even offer tips for making your arguments more persuasive.
AI-driven synonym suggestions can help you vary your vocabulary and avoid repetition. This is particularly useful when you find yourself using the same words or phrases frequently throughout your essay.
Plagiarism detection tools powered by AI can help ensure the originality of your work. Run your essay through these checks before submission to catch any unintentional similarities to existing sources.
While these tools are incredibly helpful, they shouldn’t replace your own judgment. Use AI suggestions as a guide, but trust your own voice and style. The goal is to enhance your writing, not to make it sound artificially polished or robotic.

Source: articleforge.com
Key Takeaways
Mastering argumentative essay writing involves a combination of critical thinking, research skills, and effective communication. By selecting engaging topics that you’re passionate about, you set the stage for a compelling argument.
Developing strong arguments requires more than just stating your opinion. It involves thorough research, careful consideration of counterarguments, and the ability to present your reasoning clearly and persuasively.
Structure your essay with a clear thesis, strong evidence, and thoughtful analysis of opposing viewpoints. This balanced approach demonstrates your understanding of the complexity of the issue and strengthens your overall argument.
Don’t shy away from leveraging modern tools to enhance your work. AI writing assistants can streamline research, improve language use, and help ensure originality. However, remember that these tools should supplement, not replace, your own critical thinking and creativity.
Final Thoughts
Argumentative essay writing is more than just an academic exercise. It’s a valuable skill that sharpens your ability to analyze complex issues, construct logical arguments, and communicate persuasively. These capabilities extend far beyond the classroom, proving invaluable in professional settings and civic engagement.
As you tackle challenging topics, remember that the goal isn’t simply to win an argument. It’s to explore important issues, contribute to meaningful discussions, and potentially change minds – including your own. Be open to new perspectives and willing to adjust your position as you delve deeper into a topic.
Approach each argumentative essay as an opportunity for personal growth and intellectual exploration. The research and writing process can lead you to unexpected insights and a deeper understanding of complex issues.
Continuously refine your research and writing skills. The ability to craft compelling arguments is increasingly valuable in our information-rich world. Whether you’re analyzing policy proposals, making business decisions, or engaging in public discourse, these skills will serve you well.
Consider how the critical thinking and communication skills developed through argumentative writing apply to real-world problem-solving. The ability to evaluate evidence, consider multiple perspectives, and articulate a well-reasoned position is crucial in many professional and personal contexts.
As you hone your argumentative writing skills, you’re not just preparing for academic success. You’re developing a toolkit for engaging with the complex challenges of our rapidly changing world. Each essay is an opportunity to deepen your understanding, sharpen your analytical skills, and contribute to important conversations.
Ready to elevate your argumentative writing skills? EssayWriterIQ offers comprehensive support for every stage of the essay writing process. From topic selection to final polishing, our AI-powered platform provides personalized assistance to help you craft standout essays. Visit EssayWriterIQ.com to get started today and transform your approach to argumentative essay topics.






Add comment